Given a binary tree, find the first (i.e. lowest) ancestor of two node.
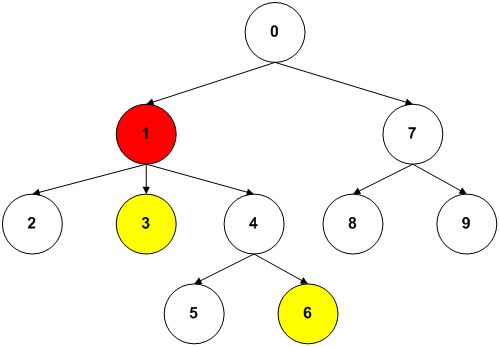
We can solve this inpalce by iterating depth first (solution 1), or by storing the path from root to each node into two Stacks, and popping items from both stacks until we find a mismatch (solution 2).

We can solve this inpalce by iterating depth first (solution 1), or by storing the path from root to each node into two Stacks, and popping items from both stacks until we find a mismatch (solution 2).
Tests
public class AncestorFinderTest {
private static final Boolean USE_ARRAY = true;
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_ancestorIsRoot() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 9, 11);
assertEquals(1, ancestor.data);
}
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_ancestorIsSecond() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 10, 11);
assertEquals(2, ancestor.data);
}
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_ancestorIsLeaf() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 8, 9);
assertEquals(5, ancestor.data);
}
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_missingNode() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 8, 13);
assertNull(ancestor);
}
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_missingBothNode() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 14, 13);
assertNull(ancestor);
}
@Test
public void findFirstAncestor_emptyTree() throws Exception {
AncestorFinder ancestorFinder = createFinder();
BinaryTreeNode tree = createTree();
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = ancestorFinder.findFirstAncestor(tree, 14, 13);
assertNull(ancestor);
}
private static BinaryTreeNode createTree() {
final BinaryTreeNode binaryTreeNode = new BinaryTreeNode(1);
// Root nodes
final BinaryTreeNode n2 = new BinaryTreeNode(2);
binaryTreeNode.left = n2;
final BinaryTreeNode n3 = new BinaryTreeNode(3);
binaryTreeNode.right = n3;
// N2 nodes
final BinaryTreeNode n10 = new BinaryTreeNode(10);
n2.left = n10;
final BinaryTreeNode n11 = new BinaryTreeNode(11);
n2.right = n11;
// N3 nodes
final BinaryTreeNode n4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4);
n3.left = n4;
final BinaryTreeNode n5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5);
n3.right = n5;
// N5 nodes
final BinaryTreeNode n8 = new BinaryTreeNode(8);
n5.left = n8;
final BinaryTreeNode n9 = new BinaryTreeNode(9);
n5.right = n9;
return binaryTreeNode;
}
private AncestorFinder createFinder() {
if (USE_ARRAY) {
return new AncestorFinderWithArrays();
}
else{
return new AncestorFinderInPlace();
}
}
}
Solution (inplace without stacks)
public class AncestorFinderInPlace implements AncestorFinder {
public BinaryTreeNode findFirstAncestor(BinaryTreeNode node, int n1, int n2){
final BinaryTreeNode ancestor = findFirstAncestorRecursive(node, n1, n2);
// If none of the nodes exist in the tree, the recursion returns null
if (ancestor == null) {
return null;
}
// If one of the nodes wasn't in the tree, the recursion will return the other node
if (ancestor.data == n1 || ancestor.data == n2) {
return null;
}
return ancestor;
}
private static BinaryTreeNode findFirstAncestorRecursive(BinaryTreeNode node, int n1, int n2) {
// Base case
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.data == n1 || node.data == n2) {
return node;
}
final BinaryTreeNode rightNode = findFirstAncestorRecursive(node.left, n1, n2);
final BinaryTreeNode leftNode = findFirstAncestorRecursive(node.right, n1, n2);
if (rightNode != null && leftNode != null) {
return node;
}
return rightNode != null ? rightNode : leftNode;
}
}
Solution (with stacks)
public class AncestorFinderWithArrays implements AncestorFinder {
public BinaryTreeNode findFirstAncestor(BinaryTreeNode node, int n1, int n2) {
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> list1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<BinaryTreeNode> list2 = new Stack<>();
getPath(list1, node, n1);
getPath(list2, node, n2);
Boolean matching = true;
BinaryTreeNode ancestor = null;
while(matching)
{
if (list1.isEmpty() || list2.isEmpty()) {
matching = false;
}
else {
BinaryTreeNode node1 = list1.pop();
final BinaryTreeNode node2 = list2.pop();
matching = node1 == node2;
if (matching)
{
ancestor = node1;
}
}
}
return ancestor;
}
private static Boolean getPath(Stack<BinaryTreeNode> list, BinaryTreeNode node, int data) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (node.data == data) {
return true;
}
if (getPath(list, node.left, data)) {
list.add(node);
return true;
}
else if (getPath(list, node.right, data)){
list.add(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
this can be done without a stack.
ReplyDelete